|
Function # |
Description |
|
100 |
Multiply A x B, Divide by C |
Note that when you run Test (Debug) Mode, the current value in SI 140 will not be displayed.
The function stores the result in SI 144.
Click on the function name to view a Help topic containing specific instructions on how to implement the function.
|
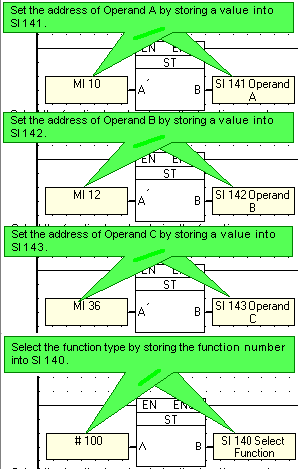
U90Ladder contains special functions that are not represented by Ladder Elements. You can perform these functions by storing values into the System Integers listed here. To implement a special function:
Note that the command number must be stored into SI 140 after the parameters are stored into the operands. |
|
The example below shows the function A*B/C, which enables the PLC to multiply 2 operand values & divide the product by a third operand.
|
|
Note that when you run Test (Debug) Mode, the current value in SI 140 will not be displayed.
The function stores the result in SI 144. |
|
Function Name |
Description |
Parameters |
Execute Function, Store into SI140 |
|
Enables PLC to multiply 2 operand values & divide the product by a third operand. |
|
|
|
|
Enables you to change the serial communication port default settings for M91 controllers. M90 models do not support this function. |
SB 141 indicates whether the COM port has been successfully initialized with the new parameters successfully: 1 = success, 0 =fail |
SI 140: 310 |
|
|
Enables PLC to receive data from external devices, such as bar-code readers, via an RS232 port. |
|
Additional Functions:
|
|
|
Sets a vector, copies source values, then writes those values into a corresponding target vector. |
|
|
|
|
Copy vector of MBs |
Sets an MB vector, copies source values, then writes those values into a corresponding target MB vector. |
|
|
|
Copies a source value, then write that value into every operand within the target vector. |
|
|
|
|
Set bit in MI vector |
Sets a bit within an MI vector |
|
|
|
Reset bit in MI vector |
Resets a bit within an MI vector |
|
|
|
Test bit in MI Vector |
Selects a bit within a vector of registers, and stores its status in an MB. |
|
|
|
Finds within vector: Mean, Minimum, & Maximum. |
|
|
|
|
Uses an MI vector to supply a GSM modem PIN code |
|
|
|
|
Causes program to stop immediately without regard to program scan |
See Interrupt for details |
|
|
|
M91 PLCs support Loadcell via I/O Expansion modules IO-LCxx. Check the Loadcell topic for details and a commands list. |
|||
|
Takes value contained in a source operand and loads that value into a target operand using indirect addressing |
|
|
|
|
Load a preset or current timer value into another operand |
SI 141 to select the timer; 0-63 |
|
|
|
Enables MODBUS Master/Slave communications |
See MODBUS for details |
|
|
|
Uses an MI vector to supply a phone number in the SMS phone book |
|
|
|
|
Store a value into a timer to change the preset or current timer value. |
|
|
|
|
Finds the square root of a number |
|
|
|
|
Temperature |
Convert C° to F° |
Degree value representation: 500 means 50.0 |
130 |
|
Temperature |
Convert F° to C° |
Degree value representation: 500 means 50.0 |
131 |
|
Function Name |
Description |
Parameters |
Activating SB-SI |
|
M91 controllers may be easily tuned via SBs. Each PID loop is linked to two SBs, one to activate auto-tune, and one that signals when the process is complete. |
auto-tune parameters are taken from the PID function |
|
|
|
Converts 16 bits or more into a integer value, or an integer value into 16 bits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The M90/91 has a special memory area containing integers that are function as a database. |
Within the database, you can access and use integers 0 through 1023 via SI 40 and SI 41. See Using the Database for details. |
||
|
Delete SMS messages from a SIM card |
SI 187, Number of SMS messages to be deleted |
Set SB 193 to delete messages (default 20 messages) |
|
|
Perform immediate actions, without regard to the program scan. |
Model-dependent; see Immediate: Read Inputs & HSC, Set/Reset Outputs for details. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Convert analog values from I/Os into decimal or other integer values |
SI 80 - 85: (x,y) variable ranges. |
Set SB 80 to activate the Linearization function. |
|
|
Load SI 87 with a value, use SBs to shift register bits left/right |
|
|
|