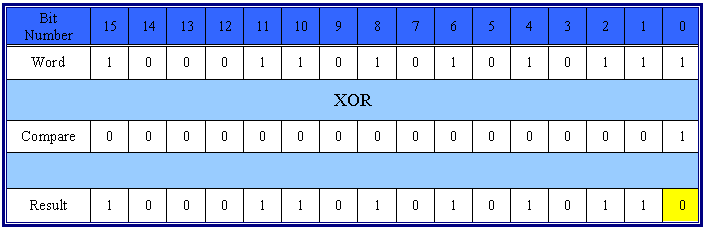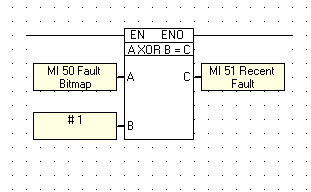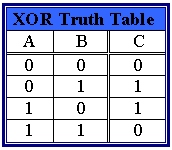
The XOR logic function block can evaluate the state of two integers to see if input A and B are equal. If either input A OR B is true - the output C will be true (logic 1). If both input A and B are true (logic 1) - the output C will be false (logic 0). If both input A and B are false (logic 0) - the output C will be false (logic 0).

Input Operands A & B must be integer values: MI, SI or # constant integer value.
Output Operand C may be a Memory Integer or a System Integer.
Use XOR to recognize changes in an integer to check for integer bit corruption. If 2 integers are equal: the result will return logic 0. If there has been bit corruption: the corrupted bit will return logic 1.