'C' Functions
You can write C functions directly in the UniLogic editor, or copy and paste code into the C Editor fields.
Use C functions in the same way you use standard ladder functions. You can call them just like standard ladder functions, reuse them, and export/import them via the Library. You can also refer to Ladder functions.
 |
Note the following limitations:
-
Within a C function, all of the declared sub-functions must be static, as well all of the global operands.
-
Within a C function, the size of all of the local variables used in that function and its sub-functions must not exceed 256 bytes.
-
Float variables are not fully supported. To use floats:
-
Your function must use inputs and outputs of the same data type (floats)
-
Use functions according to the 'C' Functions Float_Macro table shown at the end of this topic.
-
Local float variables and constants must be volatile or cast as volatile float (e.g., STORE(1,(volatile float)0.5,half)). Float function parameters require volatile cast when used as outputs in arithmetic operations.
-
Division & Modulo operations: variable divisors are not currently supported. Use these macros instead:
-
Instead of "c = a / b;" use: "ARITHMETIC_DIV(1, a, b, c);".
-
Instead of "c = a % b;" use: "ARITHMETIC_MOD(1, a, b, c);".
-
Global variables are not supported, use static variables instead.
|
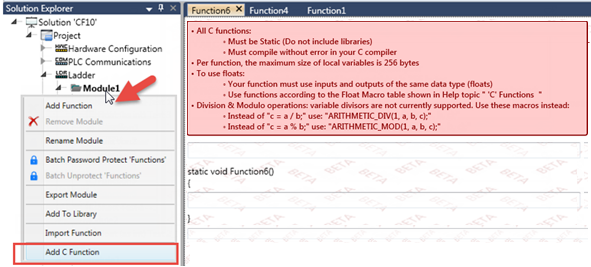
To create a function, right-click a module and select Add C Function to open the C code editor.
 |
Your C code must compile correctly in a C compiler.
|
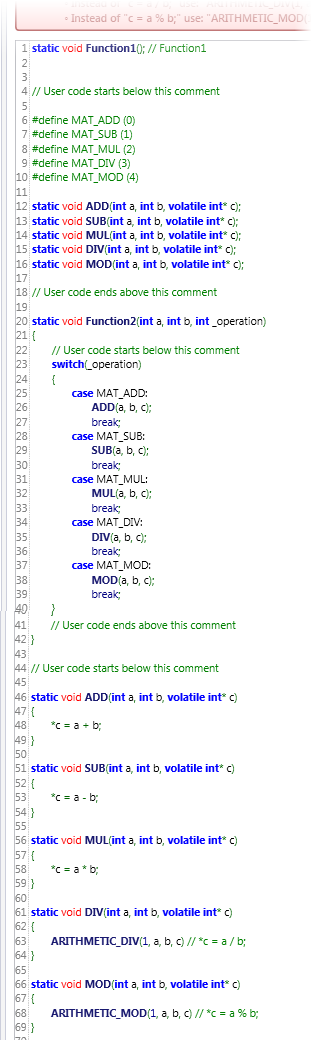
The next image shows the Forward Declaration and the Main section of a C function in UniLogic.
Float 'Macro" table
 |
All inputs and outputs of the function must be of the Float data type.
|
|
|
|
|
b = a
|
STORE(1, a, b)
|
|
a > b
|
IF_GT(1, a, b)
|
|
a >= b
|
IF_GT_EQ(1, a, b)
|
|
a == b
|
IF_EQ(1, a, b)
|
|
a != b
|
IF_NOT_EQ(1, a, b)
|
|
a <= b
|
IF_LT_EQ(1, a, b)
|
|
a < b
|
IF_LT(1, a, b)
|
|
c = a + b
|
ARITHMETIC_ADD(1, a, b, c)
|
|
c = a - b
|
ARITHMETIC_SUB(1, a, b, c)
|
|
c = a * b
|
ARITHMETIC_MUL(1, a, b, c)
|
|
c = a / b
|
ARITHMETIC_DIV(1, a, b, c)
|
|
++a
|
ARITHMETIC_INC(1, a)
|
|
--a
|
ARITHMETIC_DEC(1, a)
|
|
b = abs(a)
|
ARITHMETIC_ABS(1, a, b)
|
|
b = sqrt(a)
|
L_SQRT(1, a, b)
|
|
c = pow(a, b)
|
L_POWER(1, a, b, c)
|
|
b = log(a)
|
L_LN(1, a, b)
|
|
b = log10(a)
|
L_LOG10(1, a, b)
|
|
b = exp(a)
|
L_EXP(1, a, b)
|
|
b = sin(a)
|
L_SIN(1, a, b)
|
|
b = cos(a)
|
L_COS(1, a, b)
|
|
b = tan(a)
|
L_TAN(1, a, b)
|
|
b = asin(a)
|
L_ASIN(1, a, b)
|
|
b = acos(a)
|
L_ACOS(1, a, b)
|
|
b = atan(a)
|
L_ATAN(1, a, b)
|
|
b = sinh(a)
|
L_SINH(1, a, b)
|
|
b = cosh(a)
|
L_COSH(1, a, b)
|
|
b = tanh(a)
|
L_TANH(1, a, b)
|
Referring to Ladder Functions
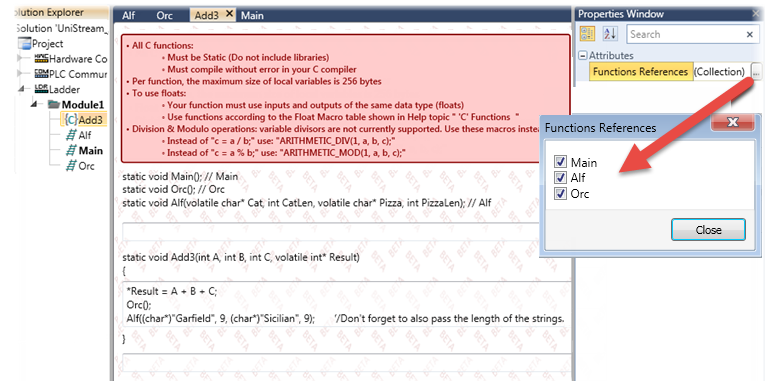
In the Properties Window:
-
Click Functions References to open the list of Ladder functions in the project.
-
Select the desired functions; the C editor displays the references.
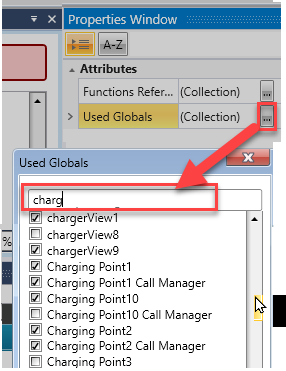
Including Used Global Tags
This enables you to view global tags in C functions via online mode, without having to pass them as a parameter.
 |
Note the following:
-
Global variables accessed through the Used Globals feature are implemented as pointers in C functions.
-
Required syntax for using global variables:
|
In the Properties Window:
-
Click Used Globals.
-
Begin typing the global name.
-
Select the desired globals; click Close.
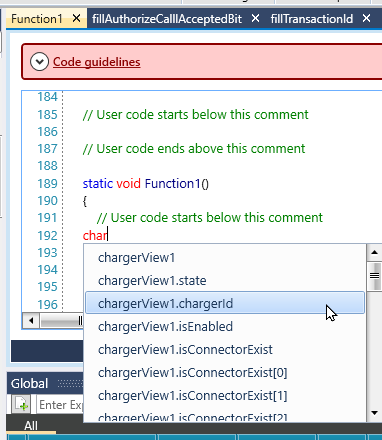
-
In the C function, begin typing the name of the desired tag; click to include it in your code.
Viewing Tag Values in Online Mode
You cannot run Online Mode and work on a C function at the same time.
When you have finished working on a C function, you can enter OnLine Mode and view the value of individual tags, as well as view all of the struct member values. Those available for viewing appear as hyperlinks; simply click the hyperlinks to view the online values.
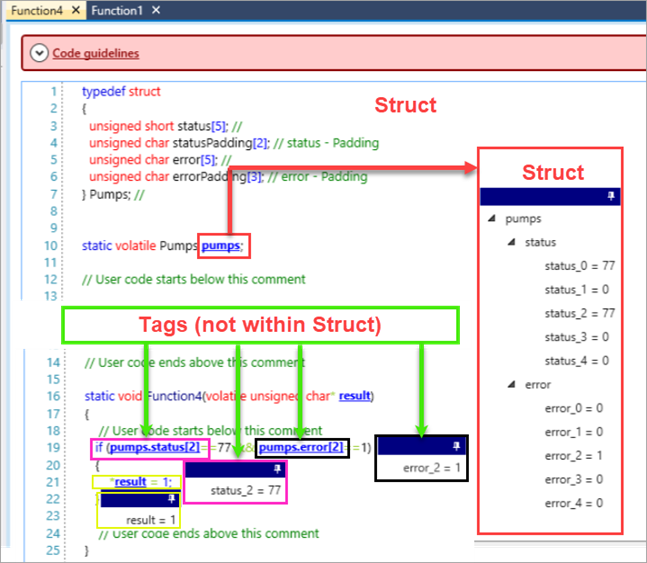
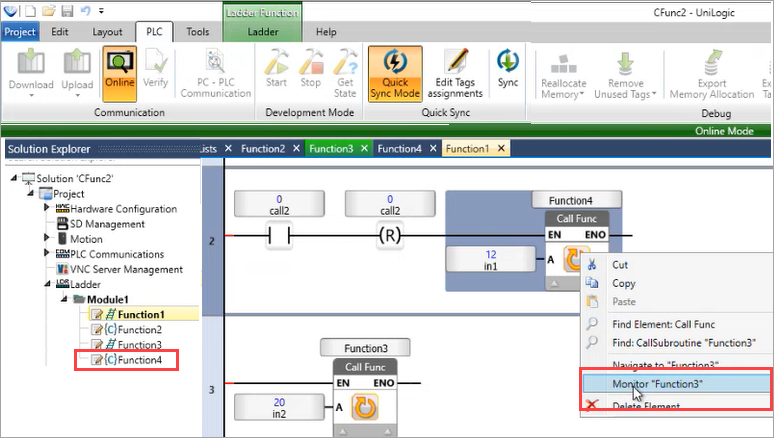
Viewing Local Tags in OnLine Mode
You can immediately view global tags in online mode. However, in order to view a function's Local tags, you need to first monitor it by right-clicking it in the Ladder that calls the function, and then selecting Monitor as shown in the next image.