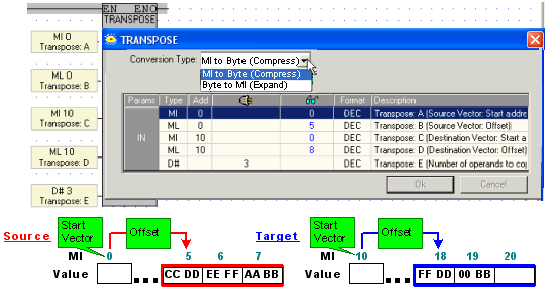
Transpose enables you to 'compress' MI values into bytes, or 'expand' bytes into MIs:
Define a source vector of registers that is offset from a selected start address.
Copy the low byte of each register within that range,
Define a target vector of operands that is offset from a selected start address.
Select Conversion type:
MI to Byte (Compress) to write the low byte of each source register into the consecutive bytes of the target vector; thus the low bytes of 3 source registers will occupy 2 MIs.
Byte to MI (Expand) to write the consecutive bytes of the source vector into the low byte of each target register, thus the bytes of 3 MIs will occupy the low bytes of 6 MIs.
|
Note ♦ |
Transpose vector maximum: MI to Bytes: 128 Bytes to MI 256 |
To use Transpose:
Click Strings on the Ladder Toolbar, then select Transpose.
Place the function in the desired net.
Select the type of function.
Link the desired Operands and Addresses.
Operand A: start address for the source vector.
Operand B: offset from the start address.
Operand C: start address for the target vector.
Operand D: offset from the start address.
Operand E: vector length.
Example:
Below, the low bytes of MI 5, 6, and 7 are copied into the consecutive bytes of MI 18 and 19.
