An Enhanced Vision that is Ethernet-enabled can function as an:
SNMP agent (slave)
SNMP Trap
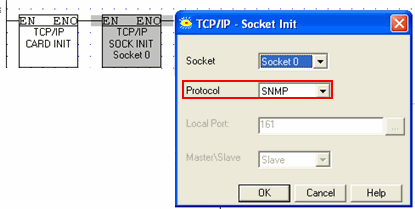
To enable the PLC to act as an SNMP agent, initialize a socket to SNMP as shown below.

This enables any SNMP manager to access operand values in the Vision via UDP, port 161. Vision supports the following SNMPv1 commands, sent to the PLC from the network:
Get
Get Next
Set
The commands support 32-bit integers.
Note that the unique PEN number assigned to Unitronics is 32481.
The figure below shows the SNMP command format.
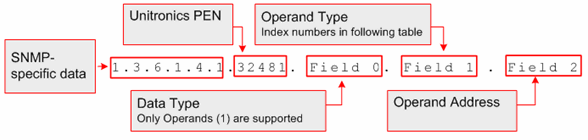
The table below shows the index numbers for operand types in Unitronics' controllers.
|
|
|
Number of Operands |
||
|
Name |
Operand type index (hex) |
V560/ERROR: Variable (V570V1040V1210) is undefined. |
V350 |
130 |
|
MB |
0x01 |
8192 |
8192 |
4096 |
|
SB |
0x02 |
1024 |
1024 |
512 |
|
MI |
0x03 |
4096 |
4096 |
2048 |
|
SI |
0x04 |
1024 |
1024 |
512 |
|
ML |
0x05 |
512 |
512 |
256 |
|
SL |
0x06 |
64 |
64 |
56 |
|
MF |
0x07 |
64 |
64 |
24 |
|
MDW |
0x10 |
256 |
256 |
64 |
|
SDW |
0x24 |
64 |
64 |
64 |
|
XB |
0x40 |
1024 |
1024 |
1024 |
|
XI |
0x41 |
512 |
512 |
512 |
|
XL |
0x42 |
256 |
256 |
256 |
|
XDW |
0x43 |
64 |
64 |
64 |
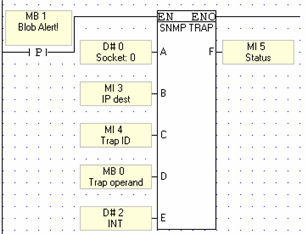
In addition, the Vision can send Trap messages in response to Ladder conditions, via the function COM>TCP/IP>SNMP Trap.
The PLC supports integer values, strings, and null.
|
Parameter |
Purpose |
|
Socket |
Select any socket |
|
IP: Target device |
The operand value will be sent to this IP |
|
Trap ID |
Use this to assign an SNMP number to the device |
|
Trap Operand |
This is the operand that is sent to the target device. If the data sent is a string, the Trap operand is the start of a vector; the PLC will send data from the vector until it reaches a null. |
|
Trap Format |
Select integer, string, or null |
|
SNMP Trap Status: |
|
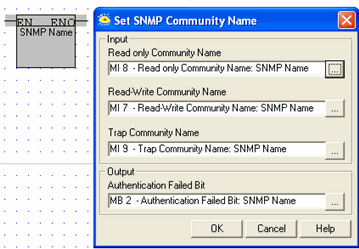
Use this function to assign the controller a name, enabling it to be accessed via SNMP.