Structs
A Struct is a container of operands. The operands may be of different data types.
There are four types of Structs:
-
System Data Tag Structs
System Data Tags service the UniStream system. These tags are organized into Structs.
-
Automatically-created Structs
These are created by the software when you add elements to your application including:
-Hardware Structs that serve hardware elements such as I/O and COM modules and modems
-Communication structs such as MODBUS and CANopen.
-Function Structs, such as PID.
-
Timer Structs
These are created when you add a Timer data tag.
-
User-defined Struct
You define these and reuse them in your program. Each instance may contain different powerup values.
-
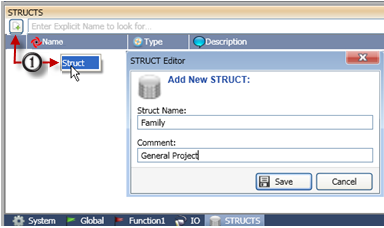
Click the Struct tab on the bottom of the Operand Window.
-
Either click the Add Struct icon, or right-click and select Add Struct.
-
Name the Struct and click Save.
 .
.
-
Either click the Add icon or right-click the window to add members to the Struct. You can add single operands or arrays, or duplicate a member.
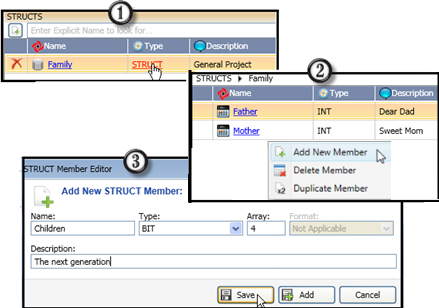
You can declare an instance of a Struct either as a global tag, or a local tag.
-
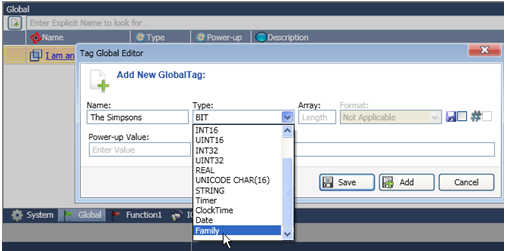
Right-click the Global Tag window, or the window of a function. Name the instance, then scroll down until you see the name of the desired Struct and select it.
-
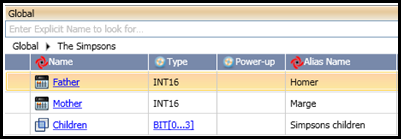
Now that the Struct is declared, you can assign Alias names to the members.
-
You can also drill down and assign Alias names to individual members within arrays that you have included in the Struct.

Now that the Struct has been declared, it can be used in your program just like any other tag.
You can right-click a Struct to duplicate it and edit its members.
Related Topics
Tags (Operands)
Data Types
Creating User-defined Data Tags
 .
.



